What Are Mushrooms Good For?
 Audrey Ferguson |
Updated on: August 22, 2023
Audrey Ferguson |
Updated on: August 22, 2023
Humans have been consuming mushrooms for health and nutrition for thousands of years, and there are literally hundreds of different medicinal uses for mushrooms of all different species. Edible mushrooms are rich in vitamins and minerals (while also being low in calories and fat), while nootropic mushrooms, even to this day, play an essential role in healing systems, particularly in Asian culture.
Today, many experts consider mushrooms a functional food. What this means is that they have benefits beyond their nutritional value. For this reason, people around the globe are becoming intrigued about fungi - particularly in the form of daily-use supplements. This article explores common uses of functional mushrooms and highlights a few of the key reasons why they are so special.
Why Mushrooms Are Essential for Health
Simply put, mushrooms are among the healthiest foods around. They are low in calories, low in fat, high in fiber, and rich in vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. The nutritional value of mushrooms varies, of course, depending on the species. However, generally speaking, edible mushrooms contain significant amounts of the following:
- B vitamins
- Vitamin C
- Calcium
- Copper
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Selenium
- Zink
Some mushrooms can also help synthesize vitamin D when exposed to UV light. Most store-bought mushrooms grow in the dark, meaning they lack this essential nutrient, but it is possible to boost the vitamin D content of supermarket mushrooms by placing them in the sun for a couple of hours before consumption. In fact, mushrooms are one of the top natural vitamin D sources for vegetarians and vegans.

Some edible mushrooms also contain a chemical called ergothioneine. This is an amino acid that has powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. A few other foods also contain ergothioneine, but button mushrooms and oyster mushrooms are some of the best sources. Many fungi also contain a group of compounds called beta-glucans, which are responsible for most of the medicinal properties of mushrooms. Beta-glucans are a type of complex carbohydrate known as polysaccharides, which have a powerful impact on the immune system.
Mushroom Health Benefits and Side Effects
Most of the benefits of medicinal mushrooms come from their potent effects on the body's immune system. Functional mushrooms contain antioxidant compounds, meaning they help rid the body of inflammation-producing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress often galvanizes an immune response, which, if left unchecked, can lead to a variety of inflammation-related side effects.
Different types of mushrooms also have specific uses, such as supporting focus and mental clarity, improving energy, and promoting a sense of calm. However, the benefits of mushrooms in each person's body will vary depending upon their unique chemical makeup.
Most people can consume mushrooms without experiencing side effects, but it is possible to have a bad reaction to certain species of fungi. For example, potential side effects of reishi mushrooms include:
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Stomach upset
- Itching
- Rash
- Headache
Certain groups of people should also be cautious when using mushroom products, such as pregnant or nursing women and those with long-term health conditions. It's also possible for mushroom supplements to interact with medications, which is why it is recommended to check with a physician before adding a functional mushroom supplement to your health routine.
Which Mushrooms Are the Healthiest?
Many different species of mushrooms have beneficial effects. But which are the best ones? Generally, mushrooms that boast the most complete range of health benefits for humans include:
Below is a brief description of each of these mushrooms and their common uses. You can find more detailed information in our in-depth guides to each species.
Reishi
Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum) is among the most recognizable functional mushrooms in the world. It is prized in East Asian medicine, where it is commonly referred to as the “Mushroom of Immortality.” Reishi is believed to promote longevity and combat signs of aging, but there is, of course, no clinical data to support these anecdotes.
Like most mushrooms, reishi contains beta-glucans for immune system support. It is also rich in chemicals called triterpenes, which give it a uniquely bitter taste. Some users also report that reishi helps to promote a state of calm and relaxation, which is why many people take it to assist in obtaining healthy sleep cycles.
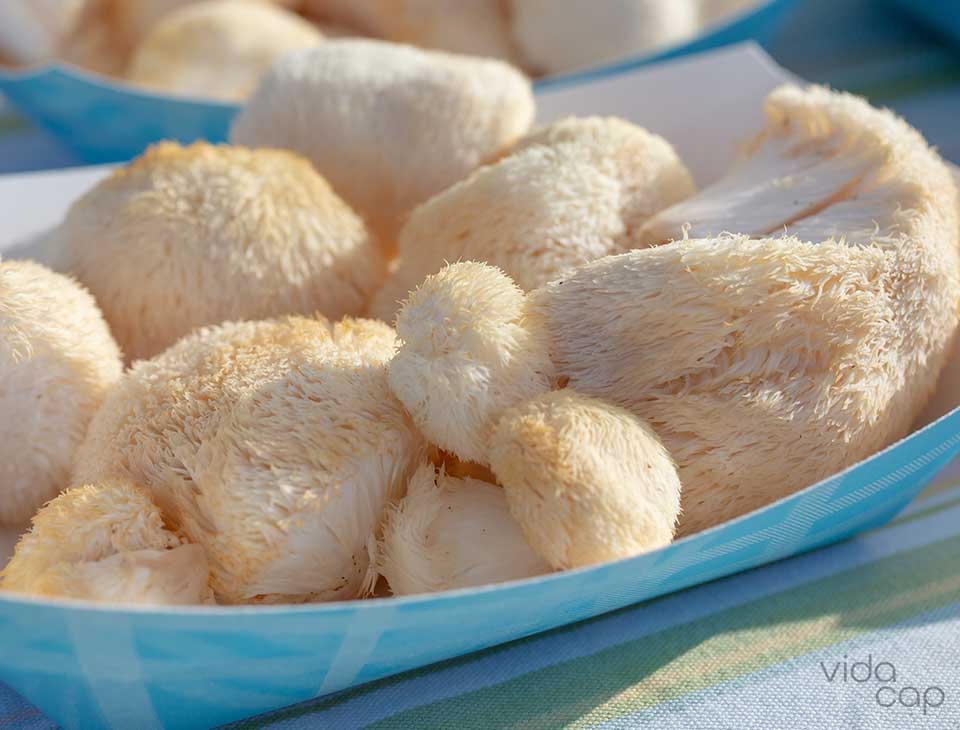
Lion’s Mane
Lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus) is another popular mushroom in East Asia culture. It is probably most famous as a gourmet mushroom with its delightful, seafood-like taste and meaty texture. In the Western world, lion’s mane is gaining attention as a nootropic. Nootropics are substances that improve mental function, including memory, concentration, and more.
Lion's mane is considered the ultimate brain food, as it contains two unique groups of compounds: hericenones and erinacines. Among other things, these compounds are known to stimulate the production of nerve growth factors in the brain, resulting in improved focus and mental clarity, decreased brain fog, and more.
Turkey Tail
Turkey tail mushrooms (Trametes versicolor) are one of the most common mushrooms in the world. They grow on rotting wood in many countries and have muted brown caps with concentric rings (just like a turkey’s tail!). However, the modest appearance of these mushrooms belies their potential usefulness, as they are considered one of the best immune-boosting fungi on the planet.
In addition to containing an array of antioxidants, turkey tail mushrooms contain two primary active compounds: polysaccharopeptide (PSP) and polysaccharide krestin (PSK). These two chemicals have been the subject of multiple clinical trials and show promising results for a variety of therapeutic uses.
Chaga
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus) is prized in Russian and northern European folk medicine. It is, in fact, however, not a mushroom at all but rather a mass of mycelial tissue known as sclerotium. Chaga grows on trees (primarily birch) and contains the triterpenes betulin and betulinic acid - both of which come from birch bark and have a range of therapeutic properties. Like other fungi, chaga is also a great source of polysaccharides. People traditionally use Chaga to support immune function, and along with lion's mane, these fungi are often regarded as one of the best all-around mushrooms for general health and wellness.
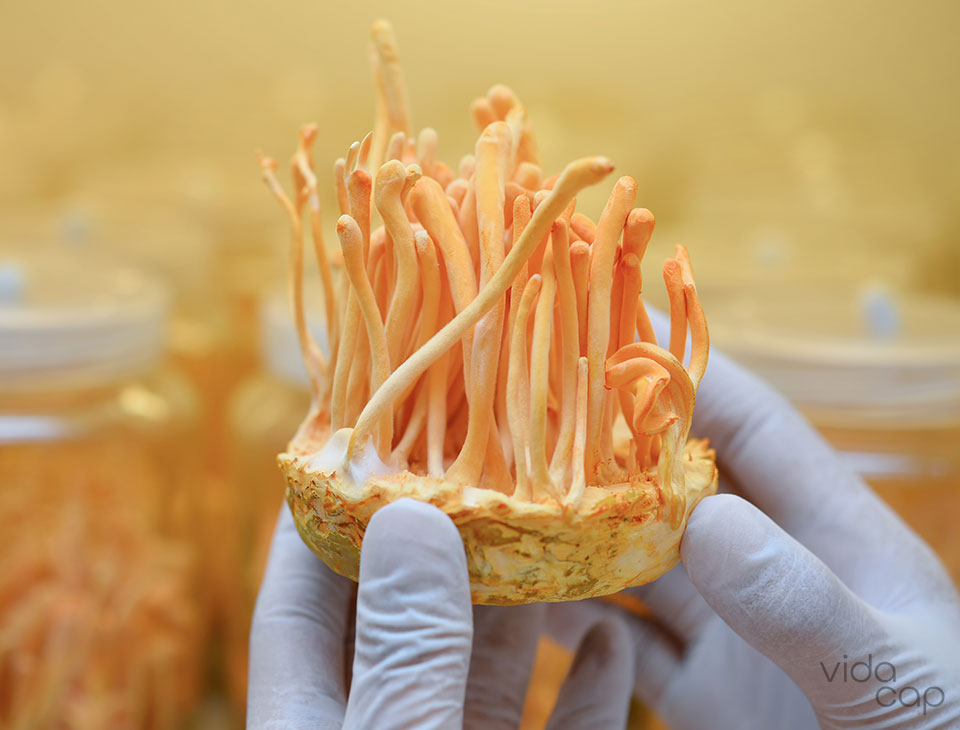
Cordyceps
Cordyceps (Cordyceps sinensis, Cordyceps militaris) is a famous mushroom that develops in the bodies of insect larvae. This strange growth habit led to its Chinese name Dong Chong Xia Cao, which means “winter worm, summer grass.”
Cordyceps grows at high altitudes in the Himalayan foothills and is extremely rare in the wild. Traditionally, this has made it one of the most expensive functional fungi around. However, scientists have learned to cultivate cordyceps, making it more accessible - and more affordable - than ever before.

Cordyceps fungi contain a chemical called cordycepin, which is known for its ability to increase energy levels and fight fatigue. For this reason, cordyceps mushrooms are popular among athletes for performance enhancement in the form of optimized blood oxygen.
The Best Way to Take Medicinal Mushrooms
In their raw, harvested form, functional mushrooms are hard and woody. Therefore, eating them like edible mushrooms is not typically an option. The most traditional way of using functional fungi involves brewing them into a tea (known as a decoction). However, there are several downsides to this method.
First, brewing tea from functional mushrooms is time-consuming; it takes at least 40 minutes to extract the active compounds, and this does not even include the time it takes to prepare, strain, and filter the brew. Second, when using functional mushrooms for therapeutic purposes, it is next to impossible to measure accurate dosing. Also, most species of functional mushrooms are very bitter (especially reishi), making them not very enjoyable to consume.
For these reasons, supplements are the way to go for those that want to take advantage of the health benefits of functional mushrooms. At VidaCap, we believe the most convenient and effective way to add functional mushrooms to your health routine is in the form of powders and capsules. Our capsules contain pre-measured doses of organic mushroom extract, and our powders are dried and ready for use in tea, coffee, smoothies, and a variety of culinary dishes.
With VidaCap mushroom supplements, there is no fuss, no mess, and no unpleasant flavor. Plus, you know you're getting the maximum bioavailability of every active compound from each of our five different fungi species. Browse our complete collection online, and start taking advantage of the life-changing benefits offered by authentic, functional mushroom supplements.
-
new
 Amanita Muscaria Mushroom GummiesCalm | Mindfulness | Balance$38 Shop now
Amanita Muscaria Mushroom GummiesCalm | Mindfulness | Balance$38 Shop now- Experience a calming and balancing buzz effect.
- 8 Delicious Berry-Mango and Citrus gummies
- 500mg amanita extract per gummy for best results
- Proudly vegan and gluten-free
- Manufactured in the USA with high-quality standards

Audrey has worked as a registered dietitian for 6 years. She graduated from the University of Florida in 2013 with a Bachelor of Science degree. In 2014 she began an internship with the Veterans Affairs Healthcare System, and was hired as an Outpatient Dietitian following graduation. She started her career counseling a variety of patients with different health concerns and disease states. After a few years into practice, she found her passion was working in cancer care, and has spent the last 4 years specializing in oncology nutrition.
In her practice, Audrey has spent a significant amount of time reviewing literature on herbal and dietary supplements in the cancer care setting. Through her work at Vidacap, she hopes to continue to expand her knowledge and understanding of the benefits of supplements in conjunction with promoting a healthy, balanced diet and management of overall health and well being.
Lynn Marie Morski
Reviewed by Lynn Marie Morski, MD, JD, who is a president of the Psychedelic Medicine Association and host of the Psychedelic Medicine Podcast. She sits on the advisory boards of Psychedelics Today, Cybin, VETS, Inc (Veterans Exploring Treatment Solutions), the Oxenberg Foundation, and the Ketamine Task Force.
Read More
 by Lynn Marie Morski, MD
by Lynn Marie Morski, MD




